Innovations in trauma surgery have significantly enhanced the management and outcomes of patients with severe injuries. Here are some of the latest advancements:
Damage Control Surgery (DCS):
This approach prioritizes rapid initial surgery to control bleeding and contamination, followed by planned, staged definitive surgeries. DCS has improved survival rates for patients with multiple traumatic injuries by focusing on stabilizing the patient first before extensive reconstructive procedures.
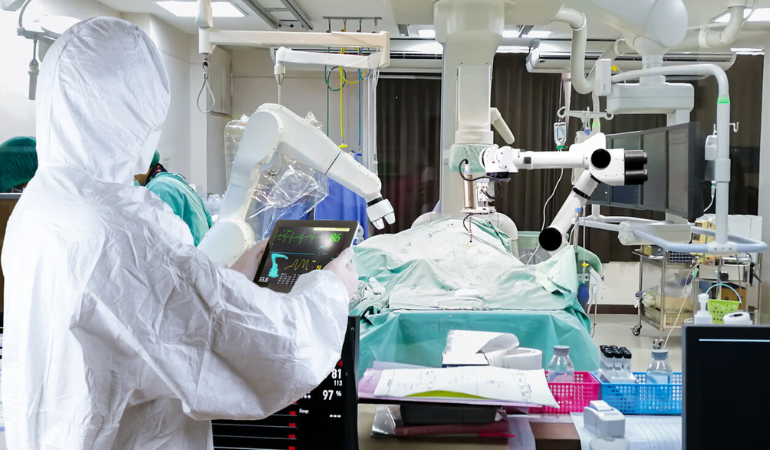
Advanced Imaging Techniques:
Innovations like portable CT scanners, 3D imaging, and intraoperative MRI provide real-time, high-resolution images. These technologies enable more accurate diagnosis and surgical planning, reducing the risk of complications during trauma surgery .
Interventional Radiology:
Minimally invasive techniques such as embolization and stent placement can control internal bleeding and repair damaged blood vessels without the need for open surgery. Interventional radiology has become a crucial tool in managing complex trauma cases .
Recombinant Coagulation Factors:
The development of recombinant coagulation factors and other hemostatic agents has improved the management of trauma-induced coagulopathy. These agents help control bleeding in patients with severe trauma, reducing mortality and the need for blood transfusions .
Point-of-Care Ultrasound (POCUS):
POCUS allows for rapid bedside assessment of trauma patients, helping to quickly identify life-threatening conditions such as internal bleeding, pneumothorax, or cardiac tamponade. This immediate diagnostic capability is crucial for timely intervention.
Advanced Wound Management:
Techniques such as negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT) and bioengineered skin substitutes have revolutionized the management of complex wounds. These methods promote faster healing and reduce the risk of infection in trauma patients .
Telemedicine and Remote Monitoring:
Telemedicine enables trauma specialists to provide remote consultations and guidance during emergencies. Remote monitoring technologies allow for continuous assessment of vital signs and other critical parameters, improving patient management in both pre-hospital and hospital settings.
Orthobiologics:
The use of orthobiologics, including bone morphogenetic proteins and stem cell therapies, has enhanced the healing of fractures and soft tissue injuries. These biologic agents promote faster and more effective regeneration of damaged tissues.
Enhanced Training Simulators:
High-fidelity simulation training for trauma surgeons using virtual reality and advanced mannequins improves surgical skills and preparedness for complex trauma scenarios. These training tools provide a realistic and risk-free environment for honing surgical techniques .
Hybrid Operating Rooms:
These ORs combine advanced imaging technology with surgical facilities, allowing for seamless transition between diagnostic and therapeutic procedures. Hybrid ORs are particularly beneficial in trauma surgery, where quick decision-making and versatile capabilities are essential.